Photovoltaics
PHOTOVOLTAICS
What is that?
It is a field of science and technology that deals with the conversion of sunlight into electricity, or in other words, the production of electricity from solar radiation using the photovoltaic phenomenon. The word photovoltaics (often incorrectly called photovoltaics ) is a combination of two words – the word photon meaning the smallest unit of solar energy and ” voltaic ” meaning the voltage that is created as a result of incident photons . It is therefore easy to conclude that photovoltaics is simply electricity generated by the sun. Photovoltaic installations do not emit any pollutants , which means that the energy obtained is fully ecological.
All electrical devices in your home or business need electricity to operate. Their universality, constant development of technology and constant increases in electricity prices result in increasingly higher costs for energy consumers . “ Solar current ” is used not only for electrical appliances, but also for heating the building in winter, cooling in summer and producing domestic hot water all year round. You can draw electricity from the grid and pay for it , but you can also produce it yourself , which makes you independent and generates real savings in your wallet . Don’t be a consumer, become a prosumer …
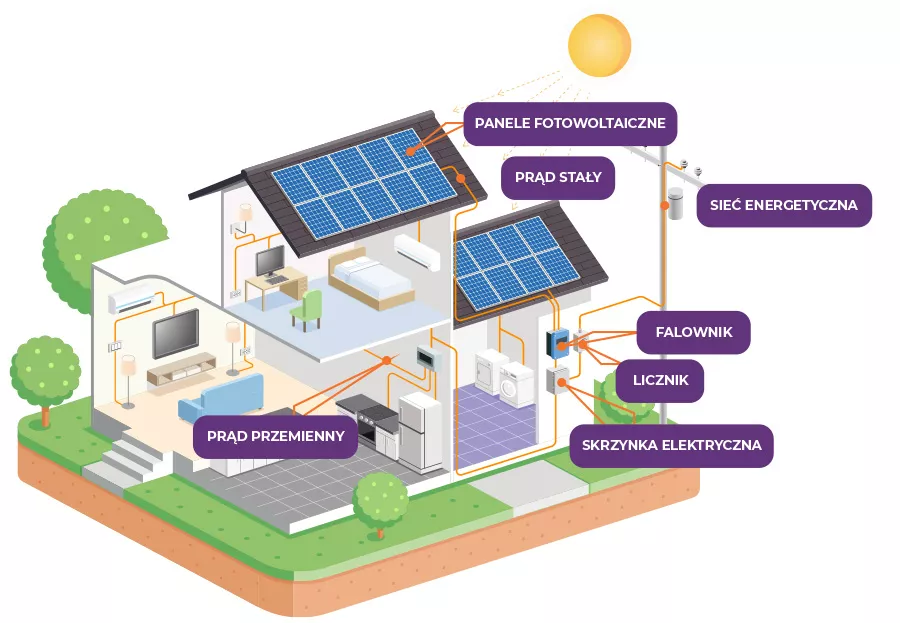
What does your own solar power plant consist of?

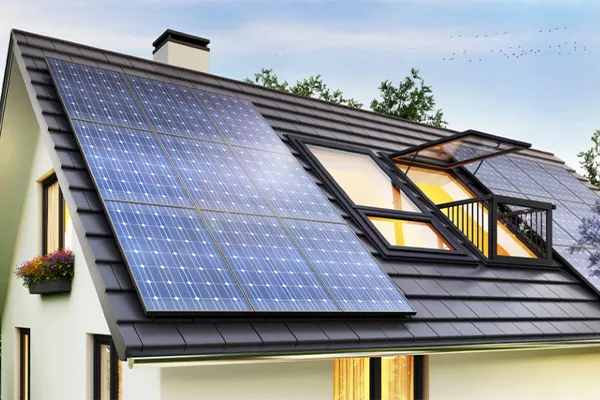
Photovoltaic modules
A photovoltaic module is a device for directly converting solar energy into electricity. It is made of interconnected photovoltaic cells and is fully protected against environmental influences. Photovoltaic modules are usually made of single cells. Cells in the form of wafers with a thickness of approx. 2 mm are made of mono- or polycrystalline silicon. This type of solar batteries are classified as so-called 1st generation and still dominate the market. What’s new are the so-called second generation cells, in which the semiconductor material is deposited in the form of a thin layer and it is often a material other than silicon, e.g. cadmium telluride ( CdTe ) or a mixture of indium, gallium and selenium (CIGS).

Inverter
An inverter, also called an “inverter”, is a specialized device responsible for transforming direct current obtained from the installation into alternating current. To put it more figuratively – PV panels draw energy from sunlight, which allows them to generate direct voltage. In the household electrical installation we have alternating current. The inverter is used to “adjust” the voltage so that the appropriate voltage is found in the sockets we use every day. To describe this process more technically, it changes DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current). The inverter works automatically in real time, so electricity is available non-stop, no different from that which is supplied by the power company in a household without panels.
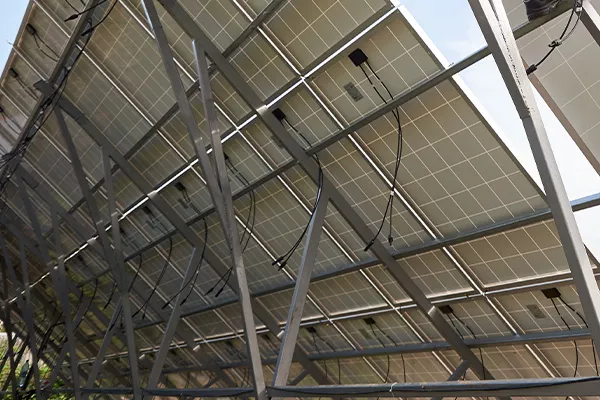

Construction
Aluminum or aluminum structure with steel elements, attached to the roof structure or mounted on the ground, which permanently holds photovoltaic modules. Depending on the roof covering and installation variant, we provide solutions dedicated to the appropriate technical conditions (e.g. roof tiles, metal roof tiles, trapezoidal sheets, structures attached to flat roofs, ballast structures, etc.).
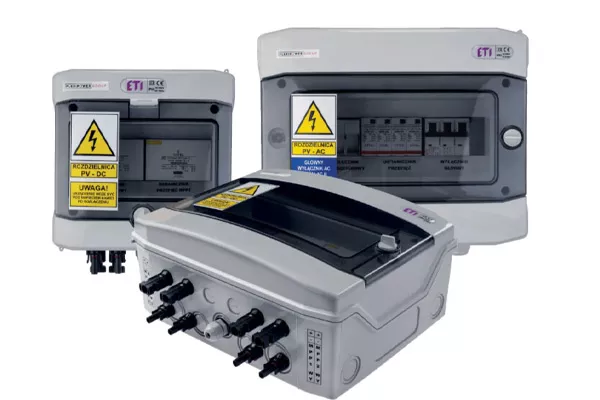

AC protection
A set of electrical devices protecting the AC and DC sides of the PV installation. Depending on the individual selection of safeguards, each installation may have a different set of safeguards. On the AC side, a 3-piece set is standard. Their task is to protect the inverter against external factors caused by anomalies in the investor’s internal installation and to protect the installation against anomalies caused by the inverter itself. AC protection is installed in a separate LV switchboard, intermediate switchboard or in the main switchboard of the facility where the photovoltaic power plant is installed.

The remaining
AC cabling discharging electrical energy from the inverter(s) to the facility’s LV network. It is designed in accordance with applicable standards and legal regulations, taking into account the conditions of cabling in the investment area, permitted voltage drop, short-circuit conditions and current carrying capacity.
DC wiring that carries away the electricity generated in the photovoltaic modules to the inverter. Specialized cabling intended for use in photovoltaic systems, characterized by increased resistance to UV radiation and increased mechanical resistance.
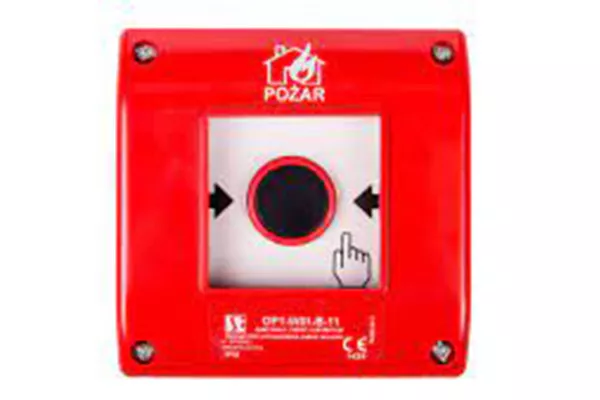

Fire protection switch and fire protection button (for installations > 6.5kWp)
Additional fire protection measures used in installations above 6.5 kWp to disconnect the DC voltage in the DC route in order to prevent the DC voltage from entering the building. Fire protection switch is an automatic switch and any loss of AC voltage or pressing the fire protection button next to the inverter will disconnect the DC circuit. Fire button – in combination with a fire switch. and the shunt trigger only supplies power to the inverter and disconnects the DC side when the glass is broken.
PRIVATE
SOLAR POWER PLANT
How it works?
1.
Sunlight falls on the photovoltaic cells from which photovoltaic panels are made.
2.
Photovoltaic panels that are mounted on your roof (or the ground) convert solar radiation (the so-called photovoltaic phenomenon occurs) into direct current energy. The efficiency of the phenomenon depends on the structure of the photovoltaic cell, the location of the panels and weather conditions.
3.
Direct current obtained from a photovoltaic panel goes to the inverter, where it is converted into alternating current, allowing you to safely power electrical devices in your home.
4.
As an energy producer, you receive a new, bidirectional electricity meter from your Distribution System Operator.
The energy obtained thanks to the photovoltaic installation “displaces” the grid current supplied by the power plant, ensuring that the current produced by the PV installation will be used first. The surplus of electricity produced from your photovoltaic installation goes to the power plant, where it is stored for you and waits until you collect it in the form of balancing (e.g. at night or in winter). If you need more electricity than your photovoltaic installation produces , the shortfall will be made up from the power grid , just as it was before the photovoltaic installation .
The photovoltaic installation is completely maintenance-free, and an application enabling monitoring is available on your smartphone or in a web browser. will show you how much energy was produced each day.
Selection of installation power and balancing (discount system)
Before we start choosing the offer or installing the photovoltaic installation itself , the most important thing is to properly select the power of the photovoltaic installation . In order to correctly calculate the demand, it is necessary to analyze the current energy consumption and forecast the annual electricity consumption in a given facility, taking into account the technical conditions on the roof, the location of photovoltaic panels towards the south, as well as energy losses due to its storage in the power plant. The size of the photovoltaic installation and the immediate payback period of the investment will depend on these parameters . Our starting point will be electricity bills, preferably with a summary of the entire last year or the last few months. We should also take into account the possible increase in demand, i.e. whether and what energy-intensive items we intend to purchase in the near future (e.g. air conditioning, induction cooker, dishwasher , electric heating , electric car, etc.). Based on this information, we can determine the approximate power of the photovoltaic installation. It is important to remember about losses in energy production due to the unfavorable location of the installation in relation to the south. These are not significant losses, but they must be taken into account to properly select the installation power.
The last element that should be taken into account when selecting the installation power is the DISCHARGE SYSTEM. In accordance with the currently applicable law, the Power Plant does not charge cash fees for storing surplus energy, but it “deducts” part of the electricity produced by the prosumer and fed into the network. This operation is referred to as the ” discount system “. For installations with a power of up to 10 kW, for 1 kWh fed into the grid, the prosumer can receive 0.8 kWh, in the case of installations with a power of 10-50 kW, the settlement takes place in a quantitative ratio of 1 to 0.7 kWh. This parameter should also be taken into account.
Installation type
(ON/OFF/HYBRID)
The solution described above is the traditional and most common form of energy storage. This system is called on grid .
Of course, there are solutions that will allow us to “cut ourselves off” from the energy system so that we are not covered by the “discount system”. This is an off grid installation ( a system operating completely outside the grid, not connected to it at all).



